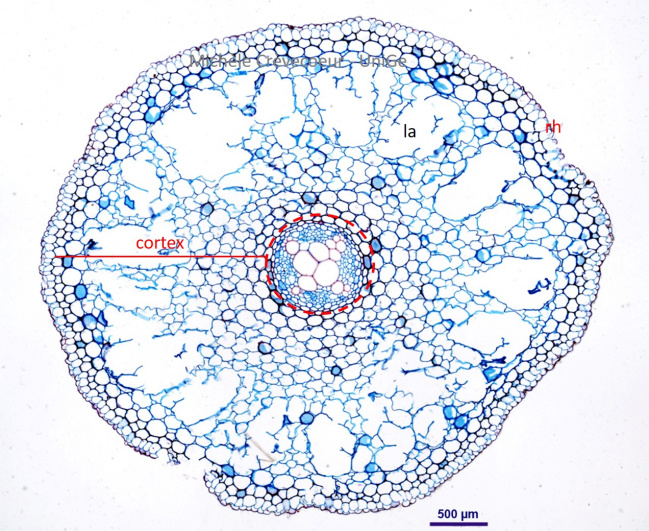
Cross section through a root of Ranunculus
Ranunculus, buttercup, is an herbaceous plant from Ranunculaceae family. It is a genus of about 600 species, among which Ranunculus asiaticus, the Persian buttercup and Ranunculus repens, a name frequently given to different species with yellow flowers. They are frequently found in meadows (meadow buttercup) and in moist soils.
The cross section illustrates the characteristics of a dicotyledon root: an extensive cortex and a small cylindrical center (dotted red lines). In the cortex we observe large lacunae (la) forming an aerenchyma typical of a root living in wet environment. The rhizodermis is uniseriate. As result of thes lacunae the cortex is more sensitve to fixation and embediing and breakings can be observed in the arenchyma.
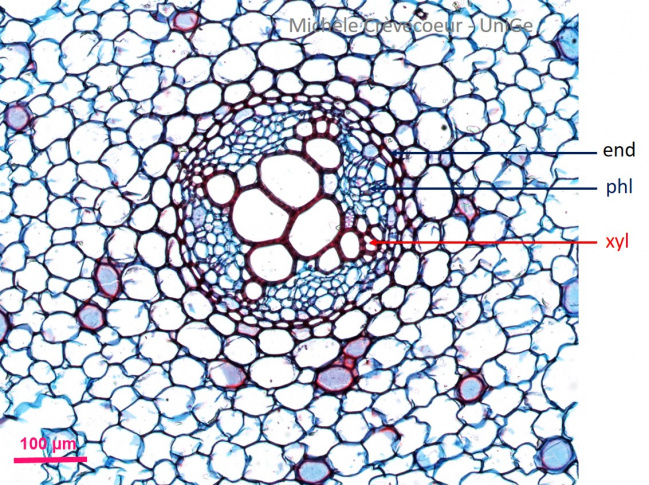
Detail of the cross section. The innermost layer of cortex is endodermis (end), with thickenings of their walls. The pericycle is discrete. Primary xylem (xyl) and phloem (phl) are distributed in alternance. The protoxylem is located towards the pericycle and large metaxylem vessels towards the center. The phloem consist in 4 oval patches of small cells with thin walls located between the 4 protoxylem poles.
All the anatomic caracterisitics on this page are typical of a young dicotyldeon root.