Morphology of the sage leaf – a bifacial leaf.
Officinalis sage is a plant in the Lamiaceae family with numerous medicinal properties. The leaves are evergreen, pale green, long, thick, opposite, oblong and pointed. They have a petiole, finely denticulated edges and a velvety texture. The two faces are covered with numerous trichomes of two types, glandular and non-glandular. On the lower/ abaxial face, veins are prominent and are different form those on the upper, adaxial face.

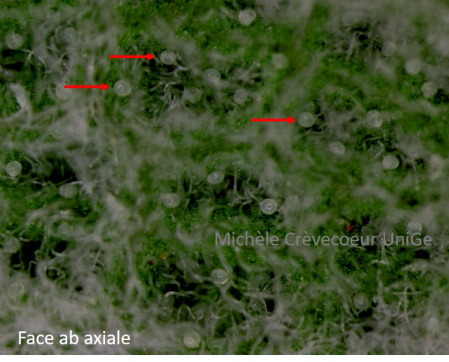
Below appearance of the two faces of the leaf imaged and photographed with a binocular stereomicroscope. The photographs illustrate the high density of both types of trichomes, with a higher density on the abaxial face. The wooly appearance of this face is well evident at level of the lamina (right picture) but also at the level of the main prominent vein (left picture). Glandular trichomes are seen in this tangle of non-glandular trichomes (red arrows bottom right).
See also Scanning Electron Micrographs of both faces of the leaf illustrated here.